The choice of a contraceptive method is a task that should be better solved with a doctor. The primary selection criteria for birth control are the effective-ness of contraception (how high is the risk of getting pregnant) and the convenience of the method used. You should also think about the side effects of the chosen method and the difficulty of quitting the birth control in case you want to get pregnant. In general, the choice of contraception depends on the woman’s age. In this article, we will review birth control for women in their 20’s.
Inexpensive Contraceptives for Women in Their 20s
Pills
This type of contraception is used by more than 70 million female half of the world’s population.
The mechanisms of action of any hormonal contraceptive are the suppression of ovulation and an increase in the viscosity of mucus in the cervix, which prevents sperm from entering directly into the uterine cavity.
There are 2 types of contraceptive pills for women aged 20-29: combined oral contraceptives (COCs) and mini-pills.
Pros:
- When used correctly, the contraceptive is effective in 95-99% of cases;
- Makes periods regular, normalizes a woman’s hormonal level;
- Prevents diseases (osteoporosis, endometriosis, malignant and good-quality diseases of the mammary glands, ovaries and uterine body);
- Relieves premenstrual syndrome (PMS), reduces dysmenorrhea;
- Improves the condition of hair, skin and nails.
Cons:
- Increases the risk of thrombosis, especially in women over 35 and smokers;
- Does not protect against sexually transmitted infections, incl. HIV infection, hepatitis, and syphilis;
- Increases the risk of intermenstrual bleeding;
- Has contraindications and side effects.
Before you want to use this or that method of hormonal contraception, you need to consult a doctor who will perform a thorough gynecological examination and also prescribe a number of laboratory and instrumental research methods to exclude you from having contraindications for using hormonal contraceptives.
Birth control pills remain one of the most effective and acceptable methods of preventing unwanted pregnancies. They may contain various combinations of hormones, for example, ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone, ethinyl estradiol and desogestrel, ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel, drospirenone and ethinyl estradiol. In addition, hormonal contraceptives also play an important role in the prevention of diseases such as menstrual irregularities, infertility, and endometriosis. In your 20s, doctors recommend using low-dose combination pills as the safest option: Iclevi, Ortho-Novum, Genora, Lo-Ovral, Modicon, Yaz, Zumandimine, Nordette, Tri-Levlen, Ovrette, Nortrel, Sprintec, MonoNessa, Estarylla, TriNessa, Ortho-Cyclen, Ortho Tri-Cyclen, Yasmin, Seasonique, Apri, and others.
Vaginal gel
In the USA, vaginal gel (spermicide) is a fairly popular method of contraception due to its ease of use and low cost.
Modern vaginal gels are made up of two components: a sperm-killing chemical and a stem. The base is responsible for the spread of spermicide into the vagina, it envelops the cervix so that no sperm can escape contact with the spermicide.
Spermicides can be used by women of any age, including in their 20s. You can use contraceptive vaginal gel during lactation, after childbirth, and after abortion.
Women use different forms of chemical contraceptives:
Birth control gel can be used alone or in conjunction with a diaphragm or cervical cap. It begins to act immediately after insertion into the vagina, the effect continues for an hour. If you use a gel together with a diaphragm or a cap, the action lasts up to 6 hours. In addition, the protective effect is noticeably increased;
The gel can be used together with condoms (at the same time!) for increased protection, as well as for protection against sexually transmitted diseases.
A good example of a contraceptive vaginal gel for women in their 20s is Shur-Seal Gel.
Pros:
- Easy to use;
- Low cost;
- Sold over-the-counter;
- Reduces the risk of sexually transmitted diseases (herpes, chlamydia, trichomoniasis);
- Prevents inflammatory diseases of the genital tract in women;
- Can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- Suitable for use by young girls and women over 20 and those cannot use hormonal drugs;
- Provides hydration when there is a lack of natural lubrication.
Cons:
- Should be applied strictly 5-10 minutes before the planned sexual intercourse;
- If sexual intercourse does occur within an hour, the product should be applied again;
- May cause allergies, rash and mucosal irritation;
- After sexual intercourse, a woman cannot take a shower or swim for an hour or any other time specified in the instructions for the drugs.

Shur-Seal Gel Review
- Active Ingredient: Nonoxynol-9
- Release Form: Vaginal Gel
- Age: 18 - 55 years
- Average Price: $30 - $40
Vaginal suppository
These contraceptives are effective, safe and relatively cheap. They have universal action and help in solving gynecological problems.
Nonoxynol (Nonoxynol-9, Encare) is the best contraceptive suppository in terms of reliability since it reduces sperm motility and the chances of conceiving a child. Nonoxynol, according to reviews, is chosen by women after 20 who want to simultaneously not get pregnant and not get gynecological diseases. Suppositories are easy to insert and do not cause discomfort. They rarely cause irritation of the mucous membrane and serious allergic reactions. One of the main advantages is the ability to use during breastfeeding.
Pros:
- A small list of contraindications;
- Small size;
- Ease of use;
- Valid for three years after manufacture;
- Can be used with a condom;
- Does not affect liver function.
Cons:
- It is necessary to strictly monitor the time of insertion;
- Rare cases of itching of the partner’s penis;
- It is not recommended to combine suppositories with other pill contraceptives.

Nonoxynol-9 Review
- Active Ingredient: Nonoxynol-9
- Release Form: Vaginal Suppository
- Age: 18 - 55 years
- Average Price: $20
Vaginal ring
Such a contraceptive for women provides reliable protection against pregnancy and is quite convenient to use. This is one of the cheapest birth control options.
The most popular vaginal rings are based on ethinyl estradiol and etonogestrel (NuvaRing, Eluryng). Be prepared to see your doctor for a prescription, as this contraceptive will not be sold without it. You may also need to see a gynecologist to insert a ring for the first time, this can be easily done on your own. Unlike other methods of birth control, this procedure should be performed only once every 3 weeks. But it is important not to get lost, as this should be done in certain cycles – on day 2-5 of your period. The ring protects against sperm activity during copulation but is ineffective against STDs.
Pros:
- Low cost;
- Safe for health;
- Doesn’t cause discomfort;
- Painless insertion;
- Rarely causes side effects.
Cons:
- The effectiveness decreases with an increase in the permissible period in the vagina;
- Requires accuracy in use;
- Has many contraindications;
- Special storage conditions;
- Requires a prescription;
- Ineffective against STDs.

EluRyng Review
- Active Ingredient: Ethinylestradiol / Etonogestrel
- Release Form: Vaginal Ring
- Age: 18 - 45 years
- Average Price: $60.00
Injection
A contraceptive injection is a hormone-containing drug that is administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously. The duration of the action is one to three months.
The active substance can be either a progestin alone or a combination of a progestin and estrogen, which interferes with egg production and thickens cervical mucus. You will need specialist help to give you an injection once a month (or one injection every 3 months). The effect of the drug is irreversible, that is, in the event of side effects, the effect cannot be stopped. The way the drug works is similar to that of an oral contraceptive or vaginal ring, except you don’t have to remember to take it daily or weekly.
Injection options include Medroxyprogesterone, Provera, Depo-Provera, and Depo-SubQ Provera 104.
Pros:
- Does not interfere with spontaneous intercourse and does not affect sensations;
- Does not require daily or weekly attention;
- Valid from 1 to 3 months;
- Can serve as an alternative to those with estrogen intolerance;
- Can be used while breastfeeding;
- May reduce premenstrual symptoms and soreness in some women.
Cons:
- You need to always get an injection in time;
- In some cases, it can cause migraines and mood swings;
- May cause headache, weight gain, abdominal discomfort;
- It may take about a year to restore full reproductive function and regular menstruation;
- Can cause a cycle violation;
- Bone density decreases when you are using the drug for more than two years without interruption;
- Does not protect against sexually transmitted infections.
Transdermal patch
The patch is a versatile and practical product for local contraception during coitus. Its use does not harm health and shows good results. A contraceptive patch is one of the most affordable birth control options.
This highly effective hormonal contraceptive usually contains ethinylestradiol and norelgestromin (Xulane). This modern contraceptive is unique and has no analogues. Its peculiarity lies in the fact that it must be glued to the skin and changed on certain days of the cycle. The maximum break should be 7 days, this protects against unwanted pregnancy. There is no need for special preparation for fixing the patch; it is enough to take a shower and wipe the skin. It can be attached to any part of the body where it will not be in close contact with clothing and hair. The only inconvenience here is the need to choose a new place for this each time, avoiding the chest.
Pros:
- Convenient release form;
- Easy to use;
- Reliable fixation;
- Effectively inhibits ovulation;
- Not felt on the body;
- Does not irritate the skin.
Cons:
- Dust can clog along the edges of the patch;
- Fights acne on the face;
- Does not protect against sexually transmitted infections.
- Required a prescription;
- Has many contraindications and special instructions.

Twirla Review
- Active Ingredient: Ethinylestradiol / Levonorgestrel
- Release Form: Transdermal Patch
- Age: 18 - 45 years
- Average Price: $3
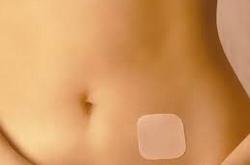
Ethinyl Estradiol / Norelgestromin Review
- Active Ingredient: Ethinyl Estradiol / Norelgestromin
- Release Form: Transdermal Patch
- Age: 18 - 45 years
- Average Price: $30 - $40
Condoms
There are two types of condoms – male and female. Condoms are the only contraceptive that, in addition to preventing pregnancy, is also a means of protecting against sexually transmitted infections.
Male condoms are considered 98% effective. They are made from thin latex, polyisoprene or polyurethane.
There are several factors that can reduce the effectiveness of condoms. These include oil-based lubricants (which can damage latex or polyisoprene condoms), condom breakage, and antistomatitis creams.
Female condoms are 95% effective and are placed inside the vagina. They are less effective as they can tear and the penis can accidentally get between the condom and the vaginal wall.
Pros:
- Available over the counter;
- Protects not only against unwanted pregnancy but also against sexually transmitted diseases, including HIV infection;
- One of the cheapest contraceptives;
- Does not require specific preparation and is used immediately before intercourse;
- Has no serious contraindications and side effects;
- Easy to use.
Cons:
- A decrease in sensitivity during intercourse, which negatively affects the quality of sexual life;
- Some men and women find its use just before intercourse unaesthetic and time-consuming.

Kurvelo Review
Ortho-Cyclen Review
Ortho Tri-Cyclen Review
Jencycla Review
Provera Review
Medroxyprogesterone Review
Ethinyl Estradiol / Norgestimate Review
Errin Review
Sprintec Review
Ethinyl Estradiol / Norethindrone Review
Microgestin 1 / 20 Review
Cryselle Review
AfterPill Review
Rugby Levonorgestrel Tablet Review
Lyza Review
Aviane Review
Morning After Review
Blisovi Fe 1 / 20 Review
Junel Fe 1 / 20 Review
New Day Review
Ovrette Review
Microgestin Fe 1/20 Review
Apri Review
Kelnor 1/35 Review
Tri-Lo-Estarylla Review
Aurovela Fe 1.5 / 30 Review
React Review
Larin Fe 1 / 20 Review
Necon 0.5 / 35 Review
MonoNessa Review
Ortho Novum 1/35 Review
Necon 7 / 7 / 7 Review
Microgestin Fe 1.5/30 Review
Cyred Review
Falmina Review
Levlen Review
Ortho Tri-Cyclen Lo Review
Tri-Lo-Sprintec Review
Gildagia Review
Alesse 21/28 Review
Balziva Review
Gildess Fe 1.5/30 Review
Previfem Review
Incassia Review
Yasmin 28 Review
Tarina 24 Fe Review
Preventeza Review
Yaz Review
Pirmella 7/7/7 Review
Aubra Review
Levonorgestrel Tablets 0.75mg Emergency Contraceptive Review
Zenchent Review
Ortho-Novum 7 / 7 / 7 Review
Opcicon One-Step Review
Lo-Ovral (21/28) Review
My Choice Emergency Contraceptive (Levonorgestrel Tablet 1.5 mg) Review
Iclevia Review
Yasmin 21 Review
Ethinyl Estradiol / Levonorgestrel Review
Loestrin 21 1.5 / 30 Review
Vyfemla Review
Estrostep Fe Review
Estarylla Review
Demulen 1/35-21/28 Review
Jasmiel Review
Chateal Review
Pimtrea Review
Tilia Fe Review
Estrostep 21 Review
Ethinyl Estradiol / Ethynodiol
Azurette Review
Emoquette Review
Zarah Review
Simliya Review
Kariva Review
Reclipsen Review
Ortho-Cept Review
Viorele Review
TriNessa Review
Mircette Review
Tri-Levlen Review
Bekyree Review
Enskyce Review
Kimidess Review
Tri-Sprintec Review
Nora-Be Review
Zovia 1 / 35E Review
Volnea Review
Microgestin 1.5 / 30 Review
Zovia 1/50E Review
Mili Review
Syeda Review
VyLibra Review
Norlyroc Review
Desogen Review
Gianvi Review
EContra EZ Review
Gildess Fe 1 / 20 Review
Junel Fe 1.5 / 30 Review
Loestrin 24 Fe Review
Nylia 7/7 /7 Review
Nikki Review
Junel 1.5/30 Review
Gildess 1/20 Review
Femcon Fe Review
Tarina Fe 1 / 20 Review
Necon 1 / 50 Review
Velivet Review
Tri-Mili Review
Taytulla Review
My Way Emergency Contraceptive (Levonorgestrel Tablet 1.5 mg) Review
Femynor Review
Tri-VyLibra Review
Philith Review
Tri-Legest Fe Review
Loestrin 21 1 / 20 Review
Tri Femynor Review
Lillow Review
Low-Ogestrel-28 Review
Pirmella 1/35 Review
Kelnor 1 / 50 Review
Afirmelle Review
Aurovela 1.5/30 Review
Alyacen 7 / 7 / 7 Review
Aurovela 1/20 Review
Desogestrel / Ethinyl Estradiol Review
Isibloom Review
Aurovela 24 Fe Review
Ortho-Novum 10/11 Review
Tri-Lo-Marzia Review
Loestrin Fe 1 / 20 Review
Necon 10/11 Review
Genora 1/35 Review
Aurovela Fe 1/20 Review
Genora 1/50 Review
Next Choice One Dose Review
Nordette 28 Review
Nortrel 0.5/35 Review
Cyonanz Review
Blisovi Fe 1.5/30 Review
Cyclafem 7 / 7 / 7 Review
Mylan Review
Brevicon Review
Enpresse Review
Hailey 24 Fe Review
Gildess 24 Fe Review
EContra One-Step Review
Zumandimine Review
Junel Fe 24 Review
Trivora-28 Review
Aftera Review
Hailey Fe 1 / 20 Review
Ethinyl Estradiol / Norgestrel Review
Levlite Review
Qlaira Review
Tulana Review
Levonest Review
Lomedia 24 Fe Review
Ayuna Review
Microgestin 24 Fe Review
Sronyx Review
Nexesta Fe Review
Nortrel 7/7/7 Review
Nylia 1 / 35 Review
Delyla Review
Alyacen 1 / 35 Review
Altavera Review
Vienva Review
Tri-Previfem Review
Deblitane Review
Levora Review
Dasetta 1 / 35 Review
Norinyl 1+35 Review
Nortrel 1/35 Review
Norethindrone Review
Portia Review
Larin 1.5 / 30 Review
Tri-Linyah Review
Fallback Solo Review
Next Choice Review
Tri-Estarylla Review
Solia Review
Junel 1 / 20 Review
Camila Review
Trinessa Lo Review
Mestranol / Norethindrone Review
Wera Review
Nor-QD Review
Modicon Review
Plan B Review
Lutera Review
Necon 1 / 35 Review
Lessina Review
Myzilra Review
Juleber Review
Blisovi 24 Fe Review
Cyclafem 1/35 Review
Larin 1/20 Review
Kalliga Review
Caziant Review
Larin Fe 1.5/30 Review
Cesia Review
Elinest Review
Larissia Review
Sharobel Review
Aranelle Review
Norlyda Review
Tri-Norinyl Review
Mono-Linyah Review
Tri-Legest Review
Ulipristal Off Label Review
Heather Review
Ortho-Novum 1/50 Review
Jolivette Review
Leena Review
Beyaz Review
Wymzya Fe Review
Triphasil Review
Ulipristal Review
Option 2 (Levonorgestrel Tablet 1.5 mg) Emergency Contraceptive Review
Plan B One-Step Emergency Contraceptive (Levonorgestrel Tablet 1.5 mg) Review
Dasetta 7/7/7 Review
Ethinyl Estradiol/Folic Acid/Levonorgestrel Review
Kaitlib Fe Review
Loestrin Fe 1.5 / 30 Review
Mibelas 24 Fe Review
Cyclessa Review
Generess Fe Review
Orsythia Review
Take Action Emergency Contraceptive Levonorgestrel 1.5mg Review
Ovral 28 Review
Ogestrel 0.5 / 50 Review
Gildess 1.5 / 30 Review
Marlissa Review
Ethinyl Estradiol / Etonogestrel
Simpesse Review
Ella Review
Ortho Micronor Review
FaLessa Kit Review
Jaimiess Review
Lo-Zumandimine Review
Jenest 28 Review
Amethyst Review
Briellyn Review
Quasense Review
Setlakin Review
Melodetta 24 Fe Review
Drospirenone / Ethinyl Estradiol Review
Ovcon 35 Review
Tri-Lo-Mili Review
Zeosa Review
Ella Review
Ovcon 50 Review
Vestura Review
CamreseLo Review
Zenchent Fe Review
Loryna Review
Lo Simpesse Review
Demulen 1/50-21/28 Review
Amethia Lo Review
Larin 24 Fe Review
Lo Loestrin Fe Review